

The Dynamics of Superbubbles in the Large Magellanic Cloud
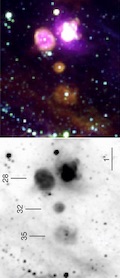
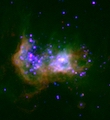
M.S. OeyBased on the stellar populations observed within this sample of LMC superbubbles, I use a numerical version of the standard, pressure-driven bubble model to investigate the shell dynamics. The results fall into two distinct categories corresponding to a subset of objects for which the observed expansion velocity is too large for the observed shell radius (``high-velocity'' superbubbles), and a subset of objects which appears more dynamically consistent with the model (``low-velocity superbubbles''). Both subsets of objects imply an overestimate in the shell growth rate equivalent to an overestimate in input power by up to an order of magnitude. The high-velocity objects exhibit X-ray evidence of supernova activity, suggesting that the dynamical discrepancy is due to acceleration by SNR impacts. 1996 ApJ, 467, 666
|

